
Virrankulutuksen optimointi on ratkaisevan tärkeää akkukäyttöisille laitteille. ST MEMS -antureiden Machine Learning Core (MLC) mahdollistaa päätöspuuluokittelun suoraan anturin sisällä, mikä vähentää mikro-ohjaimen kuormitusta ja pidentää akun käyttöikää. ST:n MEMS Studio ja AIoT Craft yksinkertaistavat tekoälypohjaista reunalaskentaa älykkäisiin ja energiatehokkaisiin sovelluksiin.
Tietyt ST MEMS -anturit on varustettu Machine Learning Core (MLC) -ytimellä, joka voi käsitellä syöttödataa (pääasiassa kiihtyvyysantureista, mutta myös gyroskoopeista ja mahdollisesti ulkoisista I2C-liitännän kautta luettavista lähteistä) ja tehdä ennusteita esikoulutetun päätöspuumallin avulla.
Päätöspuumallin suorittaminen suoraan anturin sisällä mahdollistaa tiettyjen tapahtumien tunnistamisen liikeprofiilien perusteella erittäin alhaisella virrankulutuksella. Tämä lähestymistapa vähentää mikro-ohjaimen kuormitusta, alentaa laitteen kokonaisvirrankulutusta ja pidentää akun käyttöikää.
ST tarjoaa MEMS Studio- ja AIoT Craft -työkalut, jotka auttavat käyttäjiä luomaan päätöspuihin perustuvia koneoppimismalleja MLC-yhteensopiville antureille. Mallin koulutusprosessi on suunniteltu helpoksi, joten myös käyttäjät, joilla on vähän tai ei lainkaan data-analyysin kokemusta, voivat hyödyntää sitä automaation ansiosta.
Mikä on päätöspuu?
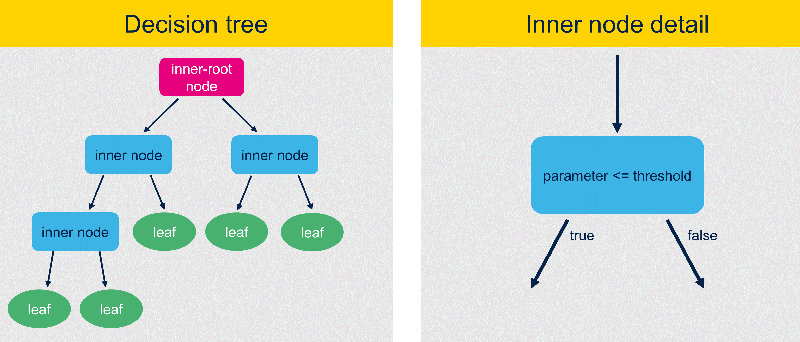
Päätöspuu on valvottu koneoppimisalgoritmi, joka käyttää binääripuu-rakennetta. ST MEMS -älyantureissa päätöspuu koostuu kahdentyyppisistä solmuista: sisäsolmuista ja ulkoisista solmuista, sekä niitä yhdistävistä oksista. Sisäsolmut sisältävät "if-then-else" -ehtoja, joiden perusteella tiedon kulku etenee kohti lopullista päätöstä.
Artikkeli on kokonaisuudessan luettavissa uudesta ETNddigi-lehdestä täällä.
BOOST EFFICIENCY WITH IN-SENSOR AI
Optimizing power consumption is crucial for battery-powered devices. With ST MEMS sensors' Machine Learning Core (MLC), decision-tree classification runs directly inside the sensor, reducing microcontroller workload and extending battery life. Discover how ST’s MEMS Studio and AIoT Craft simplify AI-powered edge computing for smarter, energy-efficient applications.
Certain ST MEMS sensors are equipped with a Machine Learning Core (MLC). This core can process input data (mostly from accelerometers, but also from gyroscopes and eventually, external data readable through the I2C interface) and make predictions using a pre-trained decision tree model. The decision tree model running directly inside the sensor can detect specific events from motion patterns with extremely low power consumption. This approach offloads the microcontroller, reduces the overall power consumption of the device, and prolongs the device’s battery runtime.
ST makes training of a decision tree more accessible through its MEMS Studio and ST AIoT Craft applications. They both help users create machine-learning models based on decision trees for MLC-enabled sensors. The model training process is also accessible to users with little or no data science experience, thanks to the automation of most of the process.
WHAT IS A DECISION TREE?
A decision tree is a supervised learning algorithm that uses a binary tree-like structure, which is also utilized in ST MEMS smart sensors. The decision tree consists of two types of nodes: inner nodes and outer nodes, along with branches. Inner nodes contain "if-then-else" conditions where a feature calculated from input data is compared against a threshold. A specific type of inner node is the root node, which carries the initial condition to evaluate and does not have any incoming branches. Branches represent the result of the inner node (true or false) and select the next node to be evaluated. Outer nodes, also called leaf nodes, do not have any outgoing branches and contain the prediction / result.
Decision trees inside ST MEMS smart sensors can be used for a wide range of applications, including activity/fitness recognition, asset tracking, or vibration monitoring.
HOW IS A DECISION-TREE MODEL TRAINED?
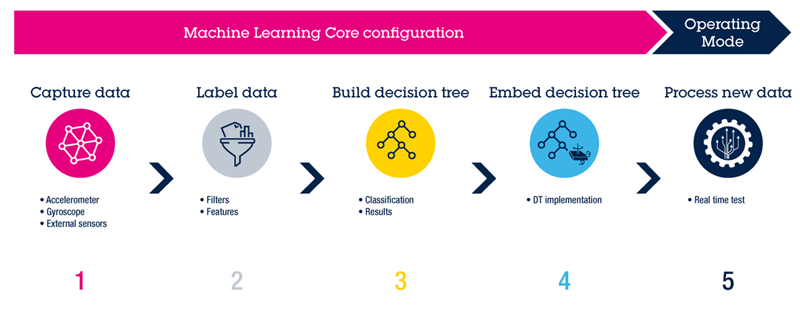
To create a decision tree, we need to:
- Define Classes: Identify the set of classes we want to predict.
- Data Collection and Labeling: Gather and tag data for each class with corresponding labels, as supervised learning requires labeled data for training.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to select useful signal features and determine the appropriate window length. Optionally, digital filters can be included.
- Feature Calculation: Calculate signal features from a specific number of samples determined by the window length. These features can include mean, variance, zero-crossing, minimum, maximum, and so on.
- Model Training: Perform model training on the selected signal features calculated from the input data.
Both MEMS Studio and ST AIoT Craft simplify the model training process, reducing the development time. The MEMS Studio is a standalone desktop application that handles the training process locally on the user’s computer. Moreover, the application includes sensor configuration and evaluation, offline data analysis, advanced embedded features, and embedded AI development. On the other hand, the ST AIoT Craft is a web-based tool focusing on AI and IoT, where all the processing is running in the cloud, allowing more flexibility.
HERE'S HOW BOTH APPLICATIONS HELP:
- Development Board Support: The tools support several ST development boards with ready-to-use firmware for data logging and model evaluation.
- Data Logging and Labeling: When using the ST AIoT Craft, data logging and labeling can be done using a web GUI or a companion mobile application. Data can also be imported in CSV format, for example, if logging was done using a different application like the MEMS Studio. In the MEMS Studio, it is possible to import data in CSV format, with data logging either by the MEMS Studio or a different application.
- Data Parsing and Labeling: the ST AIoT Craft includes utilities to help parse and label large data files. Users can visualize data in a graph, select sections, and assign corresponding labels to motion patterns. The labeled dataset can then be split into smaller logs with assigned labels, ready for training. The MEMS Studio has a separate data manipulation tool with the same capabilities.
- Automatic Analysis: The ST AIoT Craft will automatically analyze input data (selected subset of available data), select appropriate filters, features and window length. In the MEMS Studio, selected data is imported into the tool, which can be either analyzed automatically or user can manually select filters, features, and window length. It is also possible to let the tool analyze the data and then manually finetune the settings.
- Model Training and Evaluation: The tools train a decision tree and generate a sensor configuration. The trained model can be easily evaluated using selected development boards through the web GUI or a companion mobile application in case of the ST AIoT Craft, and directly in the application when the MEMS Studio is used.
Decision trees inside ST MEMS smart sensors can be used for wide range of applications.
When using the ST AIoT Craft, there is no need to install any software on your PC, as your datasets and projects are stored in the cloud. This provides more flexibility when working on your application and allows an IoT system to be set up. A preconfigured Linux gateway image, running on Raspberry Pi hardware, can be downloaded from the ST AIoT Craft website. Example projects are available for users to test the capabilities of the machine learning core.
Decision tree training flow
If you want to experience the ST AIoT Craft firsthand by either trying a project example or creating your own decision tree, please visit staiotcraft.st.com. In case a local training is preferred or you are looking for a complete all-in-one application for sensor development, get the MEMS Studio at st.com/mems-studio. You can learn more about the sensor portfolio with machine learning core capabilities and the core itself, including application notes, on st.com/mlc.
The ST AIoT Craft and MEMS Studio are part of the ST Edge AI suite, which is a collection of software tools for integrating AI features into embedded systems – edge AI. It supports a wide range of ST products, including MEMS smart sensors, and provides resources for data handling, AI model optimization, and deployment. More information and available tools and software can be found on st.com/st-edge-ai-suite.




 Teknologia19 – Aalto-yliopiston kyberturvallisuusprofessori Jarno Limnéll uskoo, että luotettavuudesta voi tulla suomalaisten yritysten suurin myyntivaltti tulevaisuudessa. – Tärkein kysymys on tulevaisuudessa, kehen ja mihin voimme luottaa. Luottamuksesta on tulossa hyvin arvokas aineeton pääoma yrityksille, Limnéll sanoi eilen messukeskuksessa.
Teknologia19 – Aalto-yliopiston kyberturvallisuusprofessori Jarno Limnéll uskoo, että luotettavuudesta voi tulla suomalaisten yritysten suurin myyntivaltti tulevaisuudessa. – Tärkein kysymys on tulevaisuudessa, kehen ja mihin voimme luottaa. Luottamuksesta on tulossa hyvin arvokas aineeton pääoma yrityksille, Limnéll sanoi eilen messukeskuksessa.









